This is a cross-post of an article I wrote for the hacks.mozilla.org blog. It shows off some of the fun stuff web developers can do with the text-shadow feature that will be released as part of Firefox 3.5.
The text-shadow CSS property does what the name implies: It lets you create a slightly blurred, slightly moved copy of text, which ends up looking somewhat like a real-world shadow.The text-shadow property was first introduced in CSS2, but as it was improperly defined at the time, its support was dropped again in CSS2.1. The feature was re-introduced with CSS3 and has now made it into Firefox 3.5.How it WorksAccording to the CSS3 specification, the text-shadow property can have the following values:none | [<shadow>, ] * <shadow>,
<shadow> is defined as:[ <color>? <length> <length> <length>? | <length> <length> <length>? <color>? ],
where the first two lengths represent the horizontal and vertical offset and the third an optional blur radius. The best way to describe it is with examples.We can make a simple shadow like this, for example:text-shadow: 2px 2px 3px #000;
A simple shadow (All of the examples are a live example first, then a picture of the working feature — so you can compare your browser’s behavior with the one of Firefox 3.5 on OSX)If you are a fan of hard edges, you can just refrain from using a blur radius altogether:
(All of the examples are a live example first, then a picture of the working feature — so you can compare your browser’s behavior with the one of Firefox 3.5 on OSX)If you are a fan of hard edges, you can just refrain from using a blur radius altogether:text-shadow: 2px 2px 0 #888;
I don’t like blurs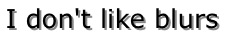 Glowing text, and multiple shadowsBut due to the flexibility of the feature, the fun does not stop here. By varying the text offset, blur radius, and of course the color, you can achieve various effects, a mysterious glow for example:
Glowing text, and multiple shadowsBut due to the flexibility of the feature, the fun does not stop here. By varying the text offset, blur radius, and of course the color, you can achieve various effects, a mysterious glow for example:text-shadow: 1px 1px 5px #fff;
Glowing text or a simple, fuzzy blur:
or a simple, fuzzy blur:text-shadow: 0px 0px 5px #000;
Blurry text Finally, you can add ”more than one shadow”, allowing you to create pretty “hot” effects (courtesy of http://www.css3.info/preview/text-shadow/ css3.info):
Finally, you can add ”more than one shadow”, allowing you to create pretty “hot” effects (courtesy of http://www.css3.info/preview/text-shadow/ css3.info):text-shadow: 0 0 4px white, 0 -5px 4px #FFFF33, 2px -10px 6px #FFDD33, -2px -15px 11px #FF8800, 2px -25px 18px #FF2200
Multiple shadows are hot The number of text-shadows you can apply at the same time in Firefox 3.5 is — in theory — unlimited, though you may want to stick with a reasonable amount.Like all CSS properties, you can modify text-shadow on the fly using JavaScript:Animated shadows with JavaScriptPerformance, Accessibility and Cross-Browser CompatibilityThe times of using pictures (or even worse, Flash) for text shadows on the web are numbered for two reasons:First, there are significant advantages to using text instead of pictures. Not using pictures saves on bandwidth and HTTP connection overhead. Accessibility, both for people who use screen readers and search engines, is greatly improved. And page zoom will work better because the text can be scaled instead of using pixel interpolation to scale up an image.Second this feature is largely cross-browser compatible:
The number of text-shadows you can apply at the same time in Firefox 3.5 is — in theory — unlimited, though you may want to stick with a reasonable amount.Like all CSS properties, you can modify text-shadow on the fly using JavaScript:Animated shadows with JavaScriptPerformance, Accessibility and Cross-Browser CompatibilityThe times of using pictures (or even worse, Flash) for text shadows on the web are numbered for two reasons:First, there are significant advantages to using text instead of pictures. Not using pictures saves on bandwidth and HTTP connection overhead. Accessibility, both for people who use screen readers and search engines, is greatly improved. And page zoom will work better because the text can be scaled instead of using pixel interpolation to scale up an image.Second this feature is largely cross-browser compatible:- Opera supports text-shadow since version 9.5. According to theMozilla Developer Center, Opera 9.x supports up to 6 shadows on the same element.
- Safari has had the feature since version 1.1 (and other WebKit-based browsers along with it).
- Internet Explorer does not support the text-shadow property, but the feature degrades gracefully to regular text. In addition, if you want to emulate some of the text-shadow functionality in MSIE, you can use Microsoft’s proprietary ”Shadow” and ”DropShadow” filters.
- Similarly to MSIE, when other, older browsers do not support the feature (including Firefox 3 and older), they will just show the regular text without any shadows.
A caveat worth mentioning is the ”drawing order”: While Opera 9.x adheres to the CSS2 painting order (i.e., the first specified shadow is drawn at the bottom), Firefox 3.5 adheres to the CSS3 painting order (the first specified shadow is on top). Keep this in mind when drawing multiple shadows.Conclusionstext-shadow is a subtle but powerful CSS feature that is — now that it is supported by Firefox 3.5 — likely to be widely adopted across the web in the foreseeable future. Due to its graceful degradation in older browsers, it can safely be used by developers and will, over time, be seen by more and more users.Finally, some words of wisdom: Like any eye candy, use it like salt in a soup — with moderation, not by the bucket. If the web developers of the world overdo it, text-shadow may die a short, yet painful death. It would be sad if we make users flinch at the sight of text shadows liketypography geeks at the sight of “Papyrus”, and thus needed to bury the feature deeply in our treasure chest.That being said: Go try it out!Further resourcesDocumentation- https://developer.mozilla.org/en/CSS/text-shadow
- http://www.quirksmode.org/css/textshadow.html
- http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-text/#text-shadow
Examples
This is a cross-post of an article I wrote for the hacks.mozilla.org blog. It shows off some of the fun stuff web developers can do with thetext-shadowfeature that will be released as part of Firefox 3.5.
The text-shadow CSS property does what the name implies: It lets you create a slightly blurred, slightly moved copy of text, which ends up looking somewhat like a real-world shadow.
The text-shadow property was first introduced in CSS2, but as it was improperly defined at the time, its support was dropped again in CSS2.1. The feature was re-introduced with CSS3 and has now made it into Firefox 3.5.
How it Works
According to the CSS3 specification, the text-shadow property can have the following values:
none | [<shadow>, ] * <shadow>,
<shadow> is defined as:
[ <color>? <length> <length> <length>? | <length> <length> <length>? <color>? ],
where the first two lengths represent the horizontal and vertical offset and the third an optional blur radius. The best way to describe it is with examples.
We can make a simple shadow like this, for example:
text-shadow: 2px 2px 3px #000;
A simple shadow

(All of the examples are a live example first, then a picture of the working feature — so you can compare your browser’s behavior with the one of Firefox 3.5 on OSX)
If you are a fan of hard edges, you can just refrain from using a blur radius altogether:
text-shadow: 2px 2px 0 #888;
I don’t like blurs
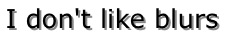
Glowing text, and multiple shadows
But due to the flexibility of the feature, the fun does not stop here. By varying the text offset, blur radius, and of course the color, you can achieve various effects, a mysterious glow for example:
text-shadow: 1px 1px 5px #fff;
Glowing text

or a simple, fuzzy blur:
text-shadow: 0px 0px 5px #000;
Blurry text

Finally, you can add ”more than one shadow”, allowing you to create pretty “hot” effects (courtesy of http://www.css3.info/preview/text-shadow/ css3.info):
text-shadow: 0 0 4px white, 0 -5px 4px #FFFF33, 2px -10px 6px #FFDD33, -2px -15px 11px #FF8800, 2px -25px 18px #FF2200
Multiple shadows are hot

The number of text-shadows you can apply at the same time in Firefox 3.5 is — in theory — unlimited, though you may want to stick with a reasonable amount.
Like all CSS properties, you can modify text-shadow on the fly using JavaScript:
Animated shadows with JavaScript
Performance, Accessibility and Cross-Browser Compatibility
The times of using pictures (or even worse, Flash) for text shadows on the web are numbered for two reasons:
First, there are significant advantages to using text instead of pictures. Not using pictures saves on bandwidth and HTTP connection overhead. Accessibility, both for people who use screen readers and search engines, is greatly improved. And page zoom will work better because the text can be scaled instead of using pixel interpolation to scale up an image.
Second this feature is largely cross-browser compatible:
- Opera supports text-shadow since version 9.5. According to theMozilla Developer Center, Opera 9.x supports up to 6 shadows on the same element.
- Safari has had the feature since version 1.1 (and other WebKit-based browsers along with it).
- Internet Explorer does not support the text-shadow property, but the feature degrades gracefully to regular text. In addition, if you want to emulate some of the text-shadow functionality in MSIE, you can use Microsoft’s proprietary ”Shadow” and ”DropShadow” filters.
- Similarly to MSIE, when other, older browsers do not support the feature (including Firefox 3 and older), they will just show the regular text without any shadows.
A caveat worth mentioning is the ”drawing order”: While Opera 9.x adheres to the CSS2 painting order (i.e., the first specified shadow is drawn at the bottom), Firefox 3.5 adheres to the CSS3 painting order (the first specified shadow is on top). Keep this in mind when drawing multiple shadows.
Conclusions
text-shadow is a subtle but powerful CSS feature that is — now that it is supported by Firefox 3.5 — likely to be widely adopted across the web in the foreseeable future. Due to its graceful degradation in older browsers, it can safely be used by developers and will, over time, be seen by more and more users.
Finally, some words of wisdom: Like any eye candy, use it like salt in a soup — with moderation, not by the bucket. If the web developers of the world overdo it, text-shadow may die a short, yet painful death. It would be sad if we make users flinch at the sight of text shadows liketypography geeks at the sight of “Papyrus”, and thus needed to bury the feature deeply in our treasure chest.
That being said: Go try it out!
Further resources
Documentation
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en/CSS/text-shadow
- http://www.quirksmode.org/css/textshadow.html
- http://www.w3.org/TR/css3-text/#text-shadow
Examples
Comments
Post a Comment